Overview
Naggy Joel is a desktop social life manager application for university students who wants to enjoy life but not at the expense of their studies. It has a GUI created with JavaFX and is optimized to allow users to interact with it through the Command Line Interface (CLI).
Naggy Joel helps users keep track of various aspects of their lives, from their social circles, to their events and deadlines. It aims to help the user be the best friend and student that they can ever be!
Summary of contributions
Major Enhancements:
-
Added the model for Schoolwork Tracker and the necessary basic commands
-
What it does: The model forms the backbone of all commands for the Schoolwork Tracker and the basic commands allow adding, deleting and editing an assignment.
-
Justification: Naggy Joel is designed to enable students to keep track of their assignments so that they can make the most out of their university life. As such, this addition is crucial as it would later be involved in some of the future enhancements.
-
Highlights: This enhancement requires an understanding of what a typical assignment should consist of so that it does not violate the law of demeter and learning of RegEx.
-
Credits: Referenced the original AddressBook and Person Model
-
-
Added the ability to allow users to generate their upcoming schedule
-
What it does: Generates the user’s schedule for a specified number of day(s) based on their stored uncompleted assignments, their individual deadlines and estimated completion time.
-
Justification: Generally, students will consider outstanding assignments and the estimated amount of time required to complete them before deciding whether they have the time to hang out with friends. However, often times there are just too many assignments and it is difficult to estimate the work hours per day for the next few days at the back of their minds.
-
Highlights:
-
Each day is colour-coded based on the estimated work hours for the day.
-
There were many cases to consider to ensure a balanced distribution of work hours to each day while ensuring that the user can still meet all deadlines and not go against the concept of time (i.e. a maximum of 24 hours a day and we cannot rewind time).
-
-
Minor Enhancements:
-
Added the ability to visualise contacts with upcoming birthdays
-
What it does: Displays all contacts with birthdays in the next 5 days (current day included).
-
Justification: As a university student with a busy life and many things to remember, often times we may unintentionally forget the birthdays of our friends and family. As such, this feature will help to serve as a reminder for users.
-
Highlights:
-
Upcoming birthdays are colour-coded based on when the contact’s birthday is and is sorted in increasing date order when displayed.
-
Displayed upon start-up and offered as a command as well.
-
Can be extended to provide gift or celebration suggestions based on stored remarks.
-
-
-
Changed the functionality of the given
editPerson command-
What it does: The enhanced
editallows users to append tags and delete individual tags. -
Justification: The original command only allows users to replace all existing tags with the new ones which is not very user-friendly as often times we want to add/delete individual tags rather than replace everything.
-
Highlights: Multiple tags can be added/deleted in the same command. Only distinct tags will be added if they do not already exist and all stated tags will be deleted if they exist.
-
-
Code contributed: [Summary of code contributions]
-
Other contributions:
-
Enhancements to existing features:
-
Documentation:
-
Contributed to both the User Guide and Developer Guide for this project.
-
-
Contribution to team-based tasks:
-
Community:
-
Over 30 Pull Requests on Github
-
Over 20 Reviews on Github
-
Helped team-members debug code and gave suggestions on how to enhance features
-
Over 15 Reported bugs and suggestions for other teams in the module
-
-
Contributions to the User Guide
Given below are sections I contributed to the User Guide. They showcase my ability to write documentation targeting end-users. |
Editing a person : (ab)edit
Edits an existing person in the address book.
Format: (ab)edit INDEX [n/NAME] [p/PHONE_NUMBER] [e/EMAIL] [a/ADDRESS] [b/BIRTHDAY] [o/ORGANIZATION] [t/TAG_TO_BE_ADDED]… [-t/TAG_TO_BE_DELETED]…
Multiple TO_BE_ADDED tags can be specified and all will be added, if it is not a duplicate.
|
Multiple TO_BE_DELETED tags can be specified and all will be deleted, if they exist.
|
To delete all tags, specify the tag-deletion prefix -t/ without any parameters.
|
Examples:
-
(ab)edit 37 a/2 Cactus Road, S903281
Changes the 37th person’s address to 2 Cactus Road, S903281. -
(ab)edit 2 n/Elysia Tan o/Comp Club
Changes the 2nd person’s name to Elysia Tan, and organization to Comp Club. -
(ab)edit 2 t/best friend -t/good friend
Removes the tag good friend from the 2nd person and adds the tag best friend to him/her. -
(ab)edit 3 e/ a/
Deletes the email and address of the 3rd person.
Schoolwork Tracker commands
Adding an assignment : (st)add
Adds a new assignment to your list of assignments.
Format: (st)add t/TITLE d/DEADLINE e/ESTIMATED_COMPLETION_TIME
Example:
-
(st)add t/CS2103 post lecture quiz d/2020-11-11 23:59 e/1
Adds an assignment titled CS2103 post lecture quiz to the Schoolwork Tracker, due 11 November 2020 23:59 PM and which takes an estimated one hour to complete. Status of this assignment is 'Uncompleted' by default.
Editing an assignment: (st)edit
Edits an assignment in the Schoolwork Tracker.
Format: (st)edit INDEX [t/TITLE] [e/ESTIMATED_COMPLETION_TIME] [d/DEADLINE] [s/STATUS]
Examples:
-
(st)edit 1 t/CS2103 Quiz e/1
Changes the title of the first assignment to 'CS2103 Quiz' and estimated completion time to 1 hour. -
(st)edit 2 d/2020-11-09 23:59
Changes the deadline of the second assignment to 9 November 2020 11:59 PM.
Deleting an assignment : (st)delete
Deletes an assignment.
Format: (st)delete INDEX
Example:
-
(st)delete 1
Deletes the 1st assignment in the Schoolwork Tracker.
Generate upcoming schedule : (st)schedule
Looks through the list of saved assignments to generate your upcoming schedule.
The schedule is generated by distributing the estimated work hours of uncompleted and not overdue assignments across several days, ranging from
query time to time that it is due. The schedule generated is based on the assumption that there is 24 hours each day to work with for days between
query date and deadline (both exclusive) and remaining time available on query date.
Format: (st)schedule n/NUM_DAYS
Example:
-
(st)schedule n/5
Displays 5 days of your generated schedule.
Contributions to the Developer Guide
Given below are sections I contributed to the Developer Guide. They showcase my ability to write technical documentation and the technical depth of my contributions to the project. |
(Elysia Tan Ziyi: 3.1, 3.2)
Schoolwork Tracker
The SchoolworkTracker helps users keep track of their assignments so that they do not accidentally overlook any of them. It consists of the AssignmentList which contains all the added assignments.
From Fig 1 below, each Assignment has four components: Title, Deadline, Status and Workload. Workload refers to the expected amount of time required to finish the Assignment. These components will be used for schedule generation when (st)schedule n/NUM_DAYS is executed (explained below).
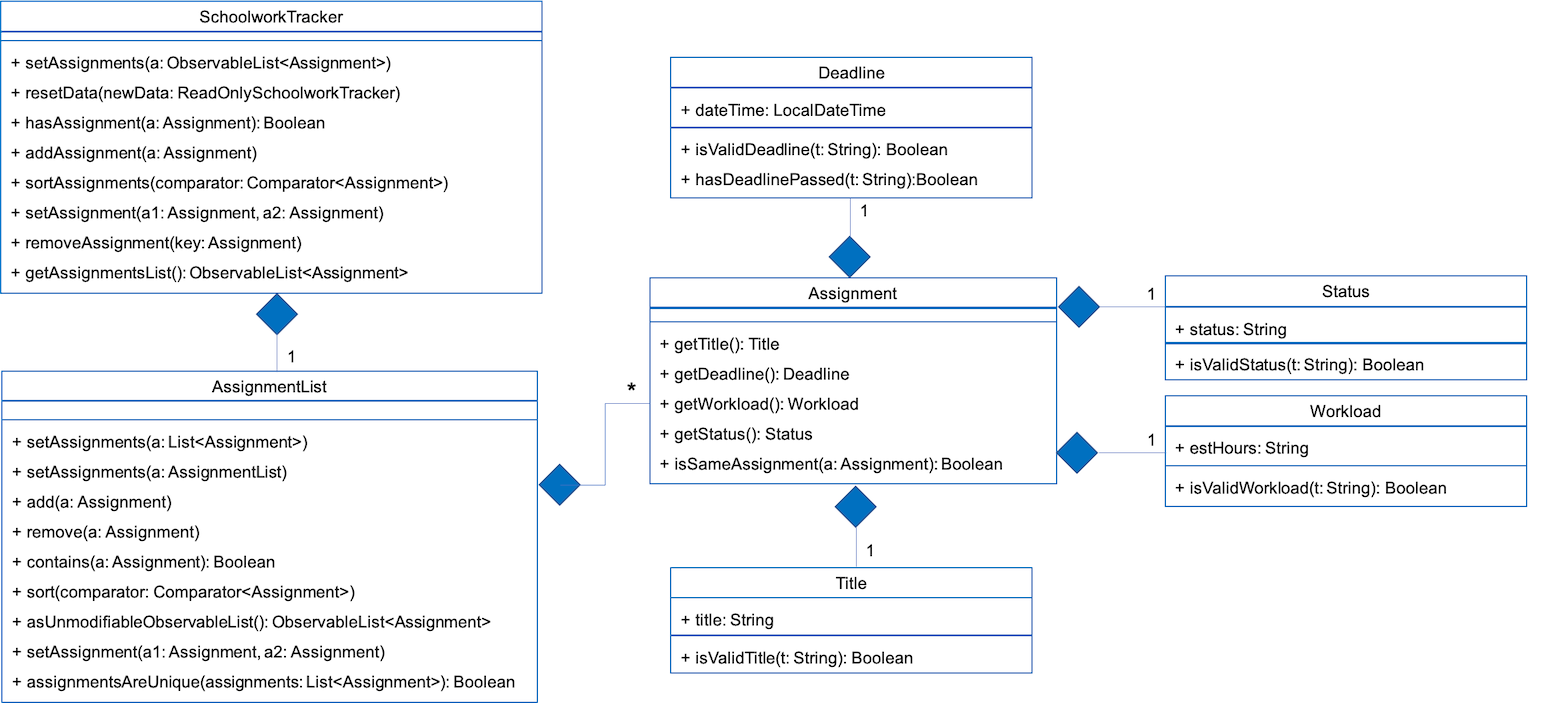
Fig 1. Class Diagram detailing the main components of the SchoolworkTracker
Schedule
Current Implementation
Schedule is facilitated by the SchoolworkTracker. This feature enhances the basic form of the SchoolworkTracker by allowing users to better visualise their current commitments so that they can better manage their time to pursue social events. This feature aims to distribute Workload as evenly as possible while ensuring that the user is able to complete the Assignment before the Deadline, unless it is impossible (i.e. Workload exceeds the amount of time the user has before the Deadline after taking into account more urgent assignments). A sample result is shown in Fig 2 below.
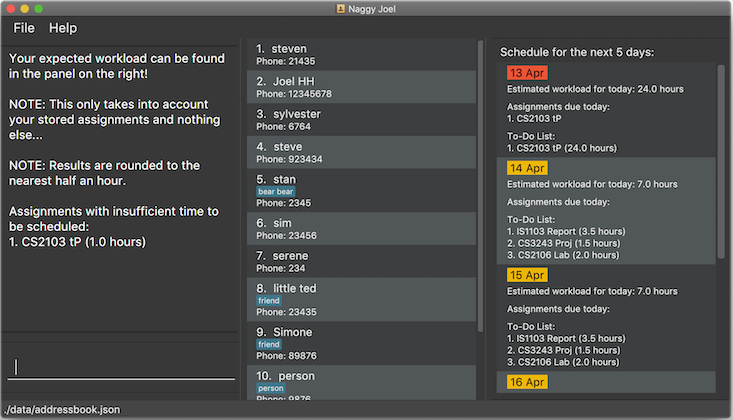
Fig 2. Sample result of the generated schedule
It utilizes the existing Assignment stored in the SchoolworkTracker and implements ScheduleList which represents the generated schedule.
As seen from Fig 3 below, ScheduleList consists of Day objects and each Day has 3 components. totalAllocatedHours represents the total number of hours allocated to the Day.
dueAssignment refers to an assignment that is due on the Day and allocatedAssignment represents an assignment that has been scheduled to be done on that Day. The latter also has an additional field allocatedHours which correspond to the suggested amount of time
that should be spent on the assignment on that Day.
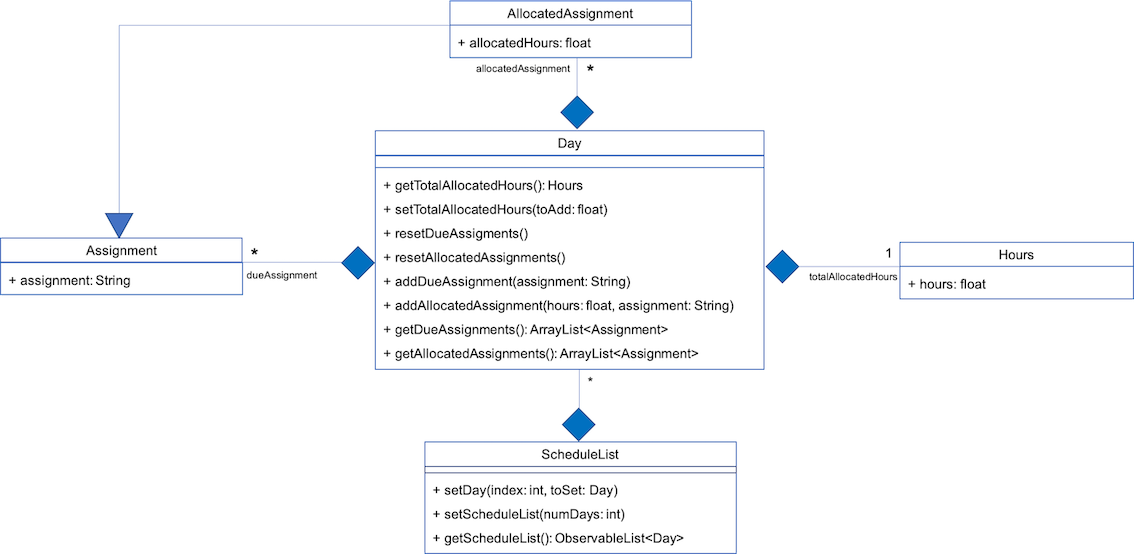
Fig 3. Class Diagram detailing the main components of ScheduleList
Given below is a detailed example of how the schedule command behaves at each stage.
Step 1: User launches Naggy Joel for the first time. SchoolworkTracker is initialized to an empty list.
Step 2: User executes the add assignment command [(st)add n/NAME d/DEADLINE e/ESTIMATED_COMPLETION_HOURS] to add assignments to the SchoolworkTracker.
Step 3: User wants to better understand his schedule for the next 5 days before deciding whether he has time to hang out with his friends and executes (st)schedule n/5.
As seen from Fig 4 below, after the user enters the schedule command, the command will first be checked for validity. If it is not valid, the user will be informed and can then choose whether to re-enter the command or enter another command. On the other hand, if the input command is valid, the application will proceed to generate his schedule and after display it on the GUI.
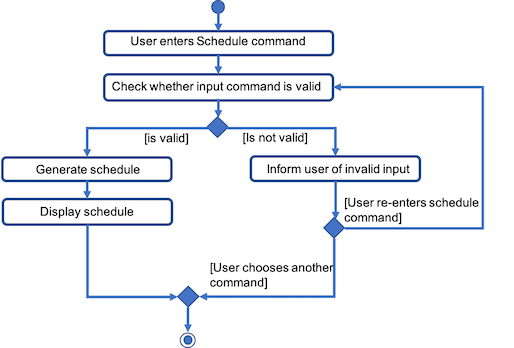
Fig 4. Activity Diagram summarizing what happens when the schedule command is entered
The specific workings of the schedule command will be explained in the paragraphs below.
As seen from Fig 5 below, arguments from the input command is first parsed using the ScheduleCommandParser which converts
the string variable into an integer and then passes it to ScheduleCommand for use later on and represents the NUM_DAYS queried. If the input argument is invalid, a ParseException
is thrown instead and the user will be notified of the proper command usage. If the command is valid, the ScheduleCommand object will be created and returned to the LogicManager who will then call the execute() method in ScheduleCommand.
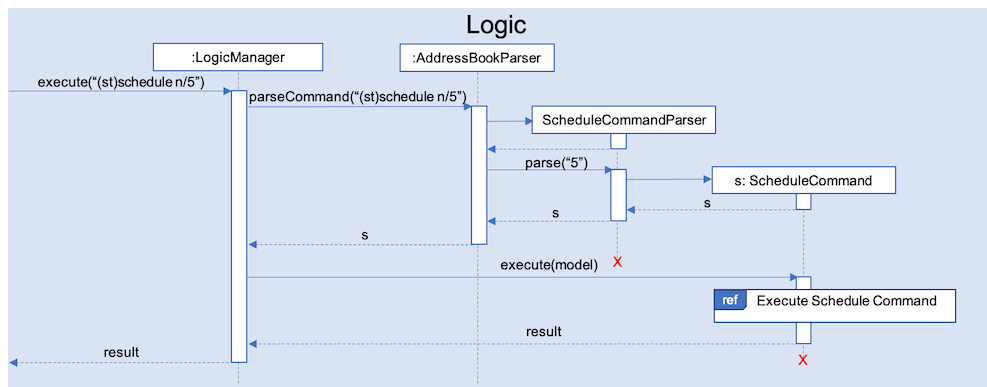
Fig 5. Sequence Diagram depicting the creation of ScheduleCommand object
As seen from Fig 6 below, the necessary preparations will be made before the schedule is being generated:
-
The
ScheduleCommandwill retrieve thefilteredAssignmentsfrom theModelcomponent. -
The
ScheduleListwill then be initialized to have a size equals to theNUM_DAYSqueried by the user, which in this example is5since the user typed(st)schedule n/5.
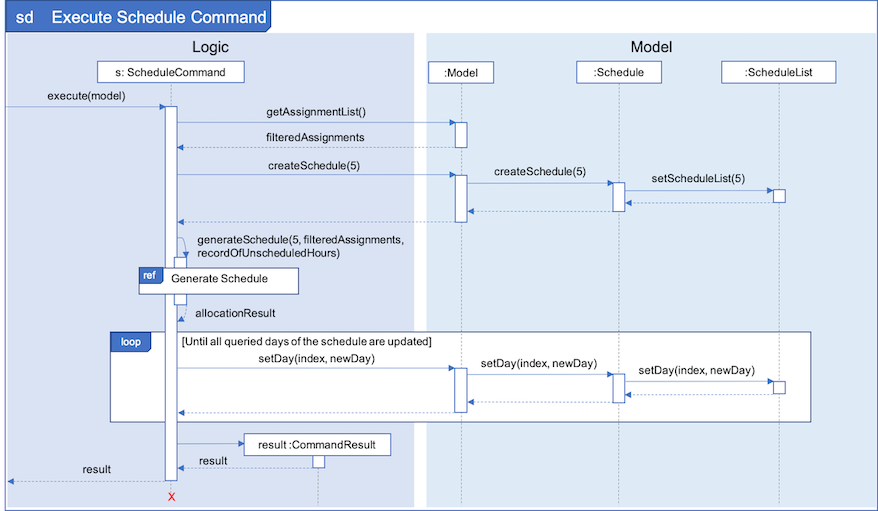
Fig 6. Sequence Diagram showing the execution of the ScheduleCommand
The schedule generation process will be explained next and begins with Fig 7 all the way to Fig 9.
In Fig 7 below, filteredAssignments is iterated through in sorted order, starting with the Assignment due the earliest and for all assignments:
-
The
StatusandDeadlineof theAssignmentwill be retrieved. -
If
Statusis uncompleted andDeadlineis not over,Workloadwill be distributed.
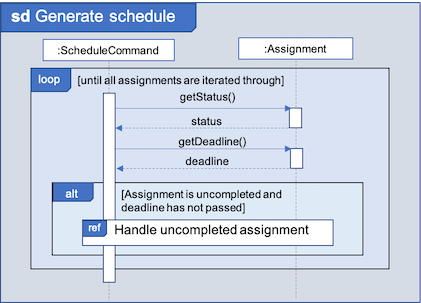
Fig 7. Sequence Diagram showing the process of generating the schedule
As shown in Fig 8 below, for each uncompleted Assignment:
-
Workloadis retrieved and distributed across several days, from query date to deadline, incrementally so as to generate a balanced schedule. -
The final allocation of hours, including amount unscheduled, is recorded and the
Assignmentwill be recorded as adueAssignmentif its deadline falls within the range of days queried.
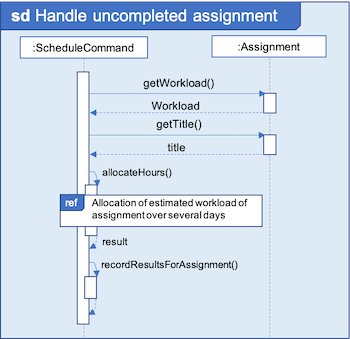
Fig 8 Sequence Diagram showing how an uncompleted Assignment is handled
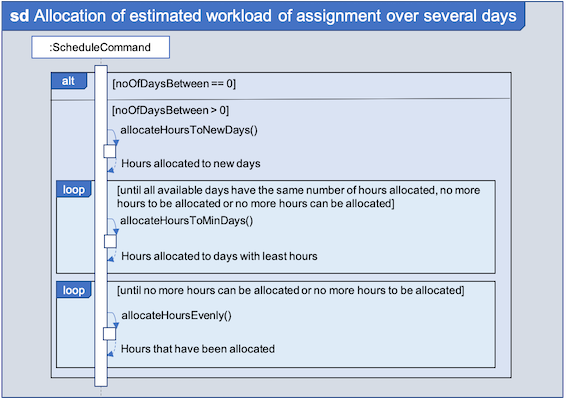
Fig 9. Sequence Diagram showing how the workload of an assignment is distributed
From Fig 9 above, assignments due on query date are handled differently from those that are not.
-
Assignmentdue on query date: The amount of time that can be allocated to the assignment will be capped at the amount of time available before theDeadline. -
Assignmentnot due on query date: Incremental distribution ofWorkloadstarting from days with no allocated hours, then days with least amount of allocated hours and lastly allocating evenly.-
Between query date and deadline (both exclusive): Available time is capped at 24 hours.
-
Query date: Available time is capped at the amount of time left in the day.
-
Deadline: Available time is capped at the amount of time before the assignment is due.
-
Actual caps are as above but after accounting for hours already allocated to other assignments.
Once the user’s schedule is generated, ScheduleList is updated with the allocationResult, a CommandResult
object will be created and returned to LogicManager. LogicManager returns it to MainWindow who
will then retrieve the generated schedule and display it as shown in Fig 10 below.
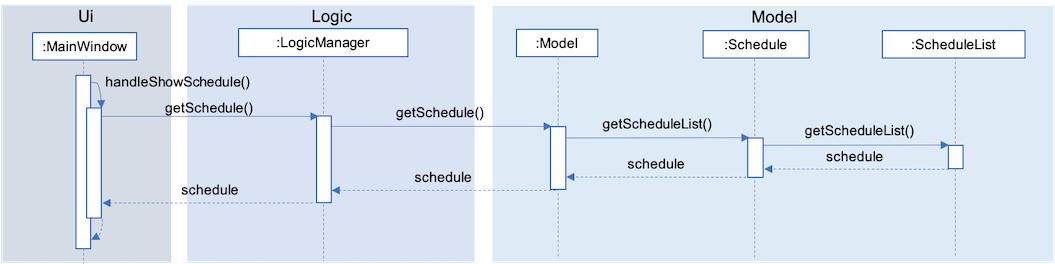
Fig 10. Sequence Diagram showing how the generated schedule is retrieved
Step 4: Based on the results, the user can then decide on how to best schedule his outing.
Design Considerations
Aspect: Distribution of estimated work hours for each assignment
-
Current choice: Hours are allocated incrementally to achieve a balanced schedule while still ensuring that deadlines can be met (unless impossible due to the constraints of time left)
-
Pros: Better reflects the real-world scenario where students are more likely to spread out their work and encourages work life balance which is the main selling point of Naggy Joel.
-
Cons: Complicated algorithm is more prone to errors.
-
-
Alternative: For each day, cumulatively add
Workload divide by Number of days to deadlinefor all assignments-
Pros: Easier to implement.
-
Cons: Some days may have impossibly high workload, deadlines are not handled properly.
-
Aspect: Variable type to be used for calculations during distribution of workload
-
Current choice: Use of BigDecimal for calculations
-
Pros: More accurate allocation of hours while minimizing lost hours due to rounding errors.
-
Cons: Harder to handle and new objects have to be created each time.
-
-
Alternative: Restrict calculations to the use of integer
-
Pros: Easier to handle and more accurate comparisons can be made as compared to when floats are used as floating point arithmetic is not exact.
-
Cons: A lot of unnecessary ‘loss’ in allocated and available time due to rounding errors.
-